Libplanet
Posted on
What is Libplanet?
Libplanet is a .NET library for creating multiplayer online game in decentralized fashion, which means the whole gameplay occurs on a peer-to-peer network among equal nodes rather than an authorized central server. Under the hood, it incorporates many features (e.g., digital signature, BFT consensus, data replication) of a blockchain.
It has competitive advantages over other solutions for decentralized gaming:
-
Embeddable
- A game app does not have to communicate with another running process, hence it doesn’t require extra marshaling or processes management.
-
Isomorphic
- Libplanet is a .NET library, so every game logic can be written in the same language, C#, and run on the blockchain. No glue code or “smart contracts” are needed.
-
Token-independent
- Unlike almost every blockchain system, it does not force users to create and deal with yet-another-cryptocurrency. Your game can be free to play, and enjoyed by regular gamers.
How it works?
Action-Based State Management
In Libplanet, game state changes are driven by actions. For example, when a character levels up, the action (e.g., completing a quest) is recorded and propagated, not just the resulting state. These actions are grouped into transactions, which are then stored in blocks on the blockchain. This approach ensures that all nodes can independently verify and reconstruct the game state by replaying the sequence of actions.
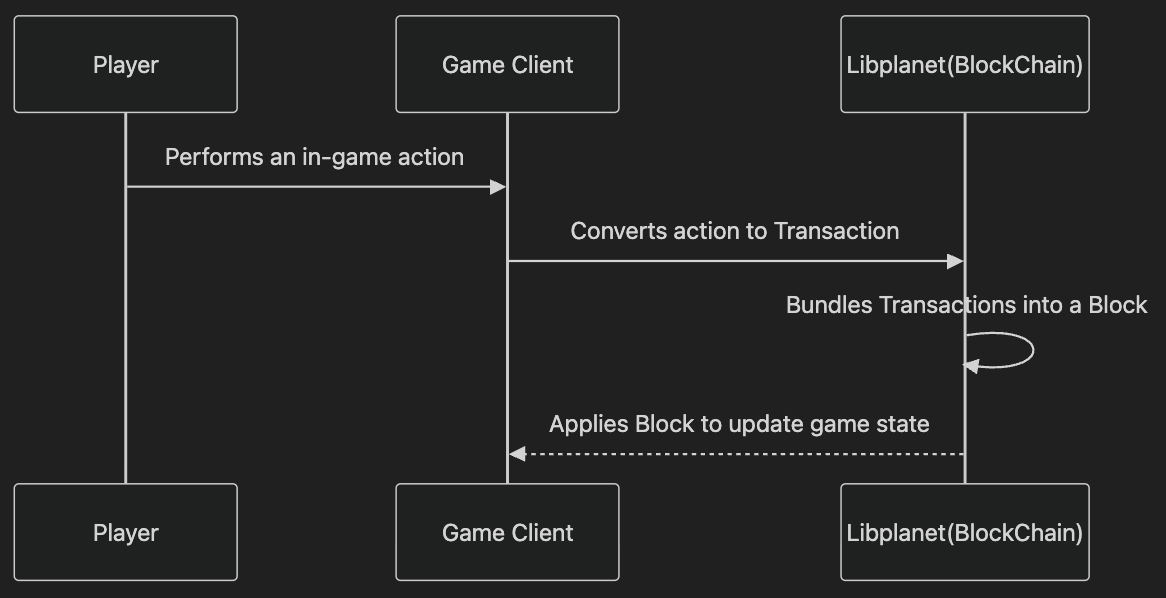
Blockchain and Consensus
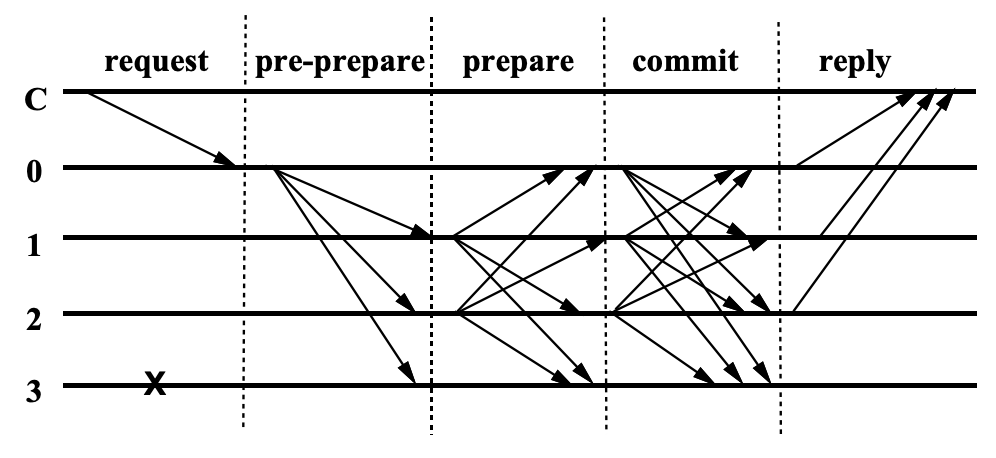
Libplanet employs blockchain technology to maintain a consistent and tamper-resistant game state across all nodes. It incorporates features like digital signatures and Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) consensus algorithms to ensure data integrity and agreement among participants.
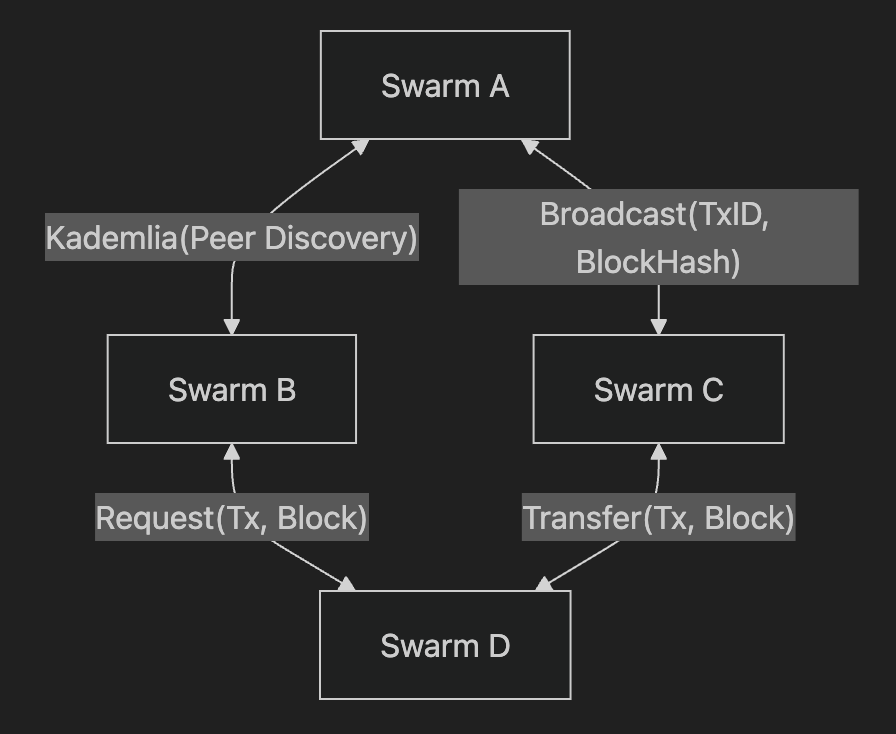
Networking and Peer Discovery
To facilitate communication in a decentralized environment, Libplanet utilizes the Kademlia Distributed Hash Table (DHT) protocol for efficient peer discovery and message routing. This allows the network to scale effectively as more players join.
Additionally, Libplanet supports NAT traversal using TURN (Traversal Using Relays around NAT) servers, enabling peers behind firewalls or NATs to connect seamlessly.
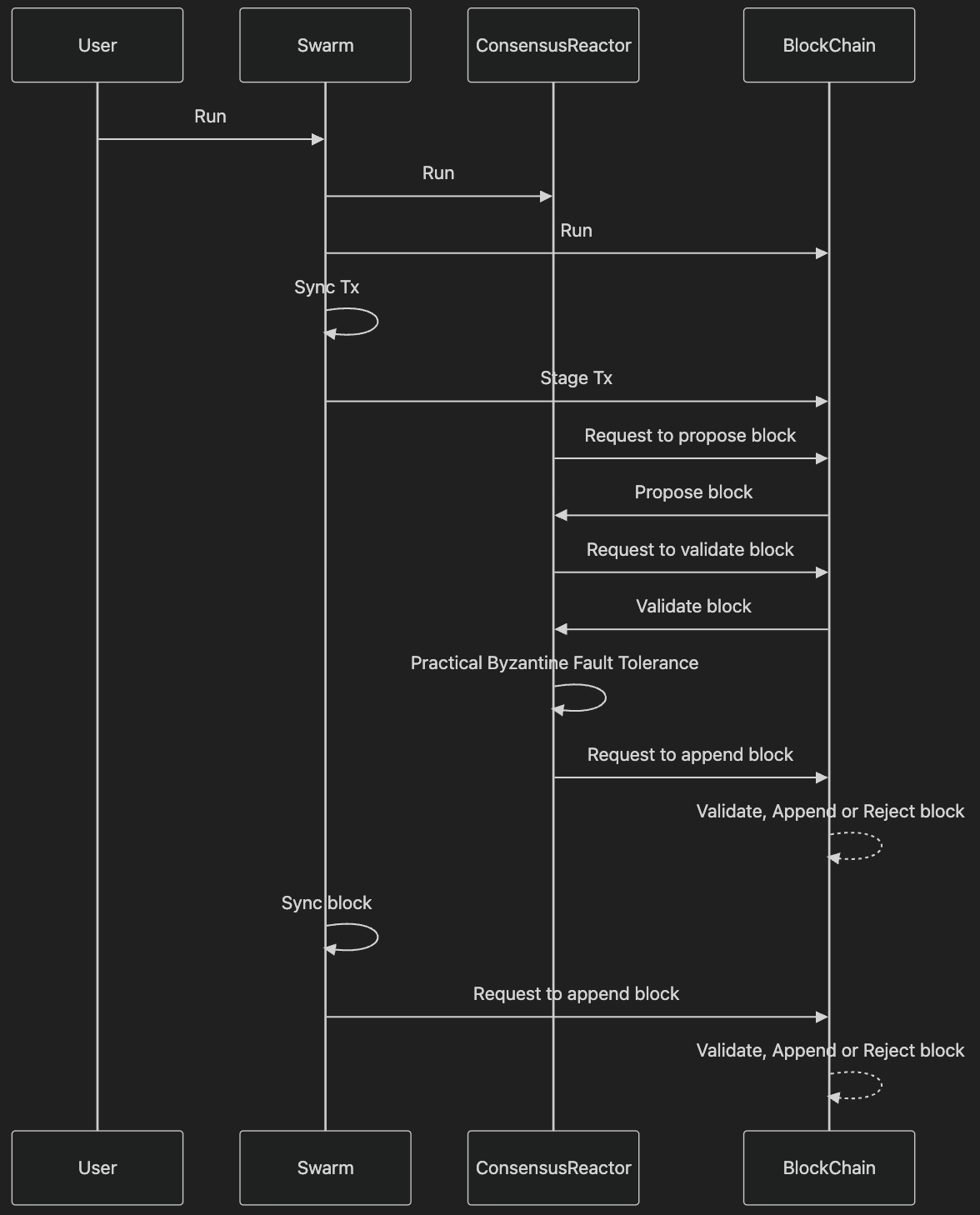
Practical Implementation
To build a game using Libplanet, developers typically instantiate two main classes:
BlockChain: Manages the creation and validation of blocks, maintaining the sequence of actions that define the game state.
Swarm: Handles peer-to-peer networking, including the broadcasting and receiving of blocks and transactions among nodes.
These components work together to ensure that all game clients remain synchronized without the need for a central server.
Use Case: Nine Chronicles
Nine Chronicles is a notable example of a game built entirely on Libplanet. It operates as a fully decentralized online RPG where players can craft items, trade, and engage in battles, all without centralized servers. The game’s design leverages Libplanet’s capabilities to ensure that the game world persists and evolves based on player actions, even if some nodes go offline.
Conclusion
Libplanet offers a robust framework for developing decentralized multiplayer games, providing tools for action-based state management, secure consensus, and efficient networking. By removing the dependency on centralized servers, it empowers developers to create games that are resilient, transparent, and community-driven.